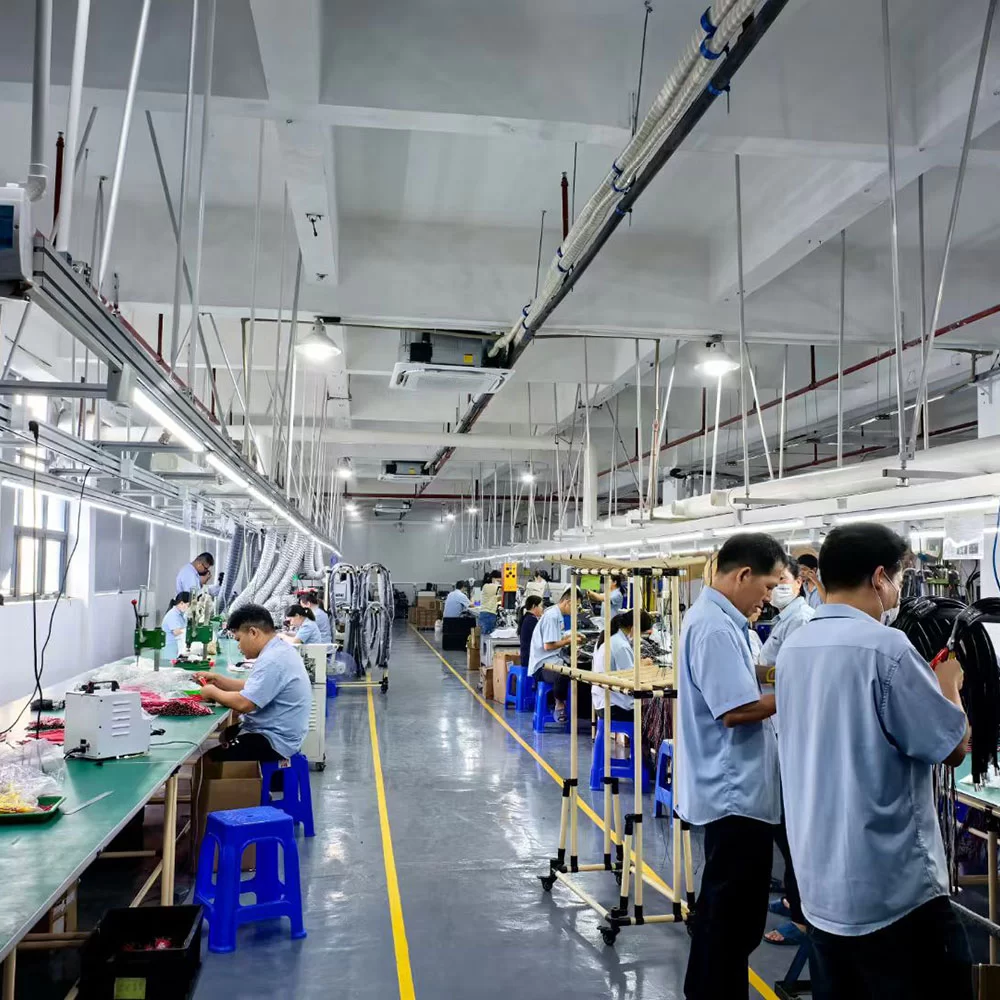
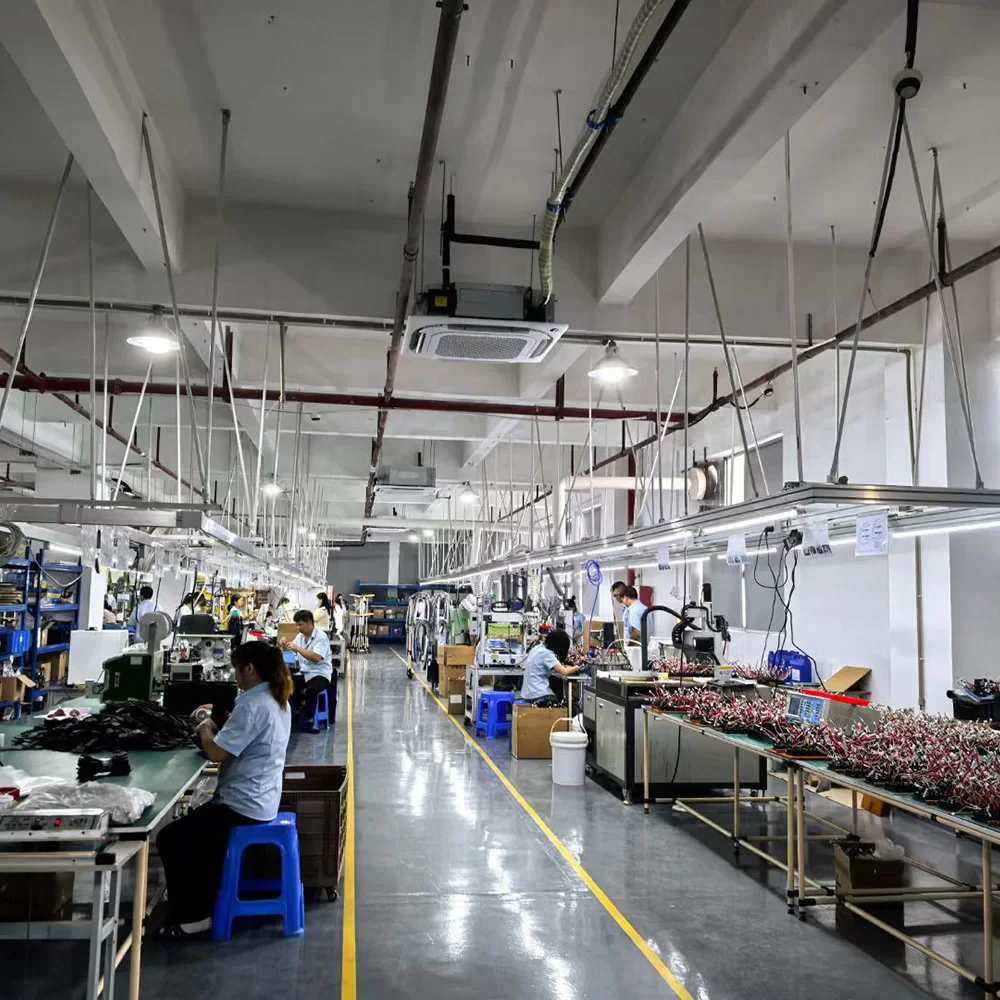
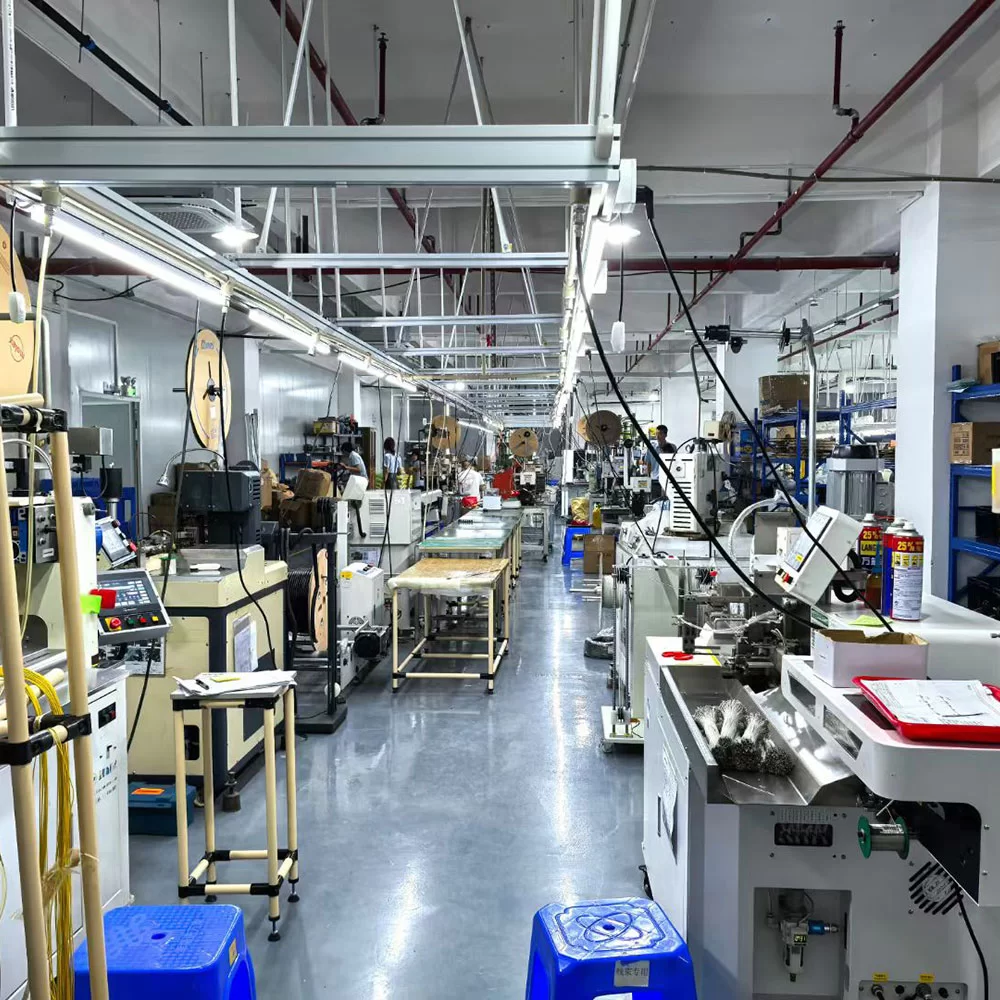
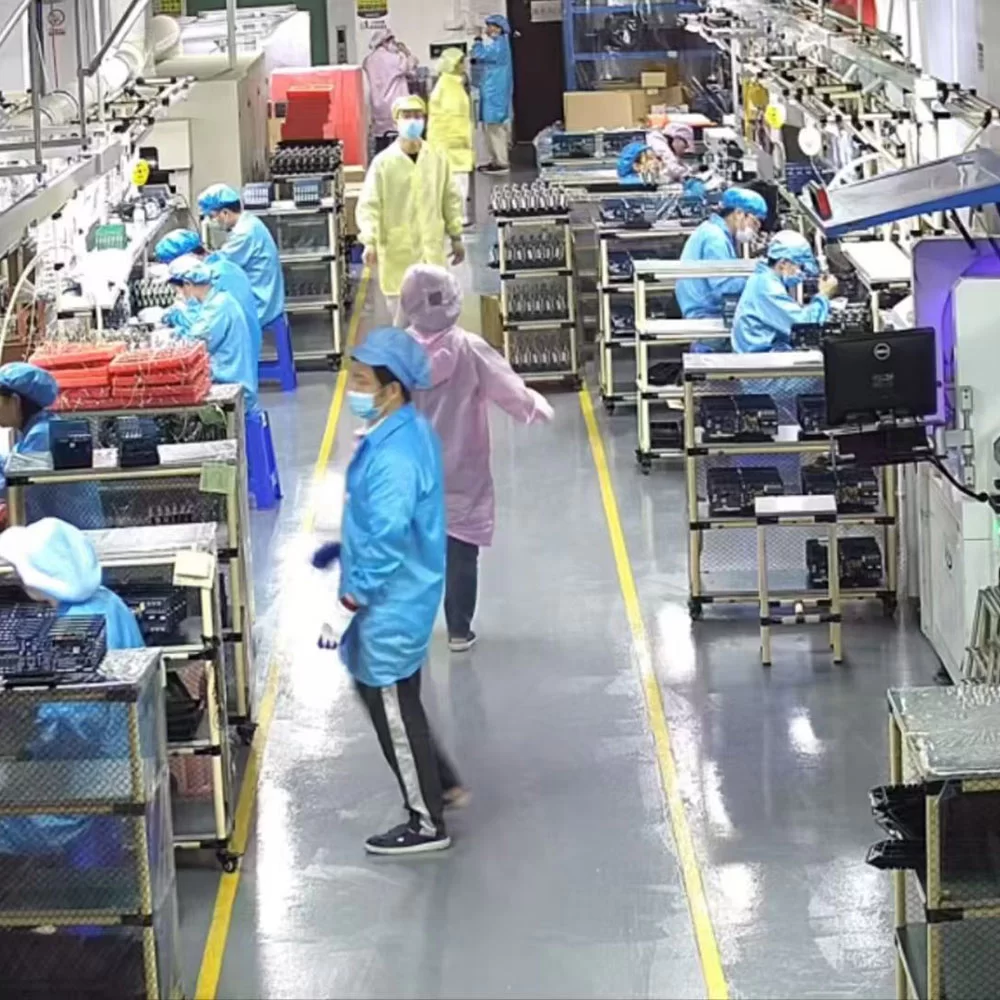
Cable & Wire Harness Assembly Services
Cable & Wire Harness Assembly
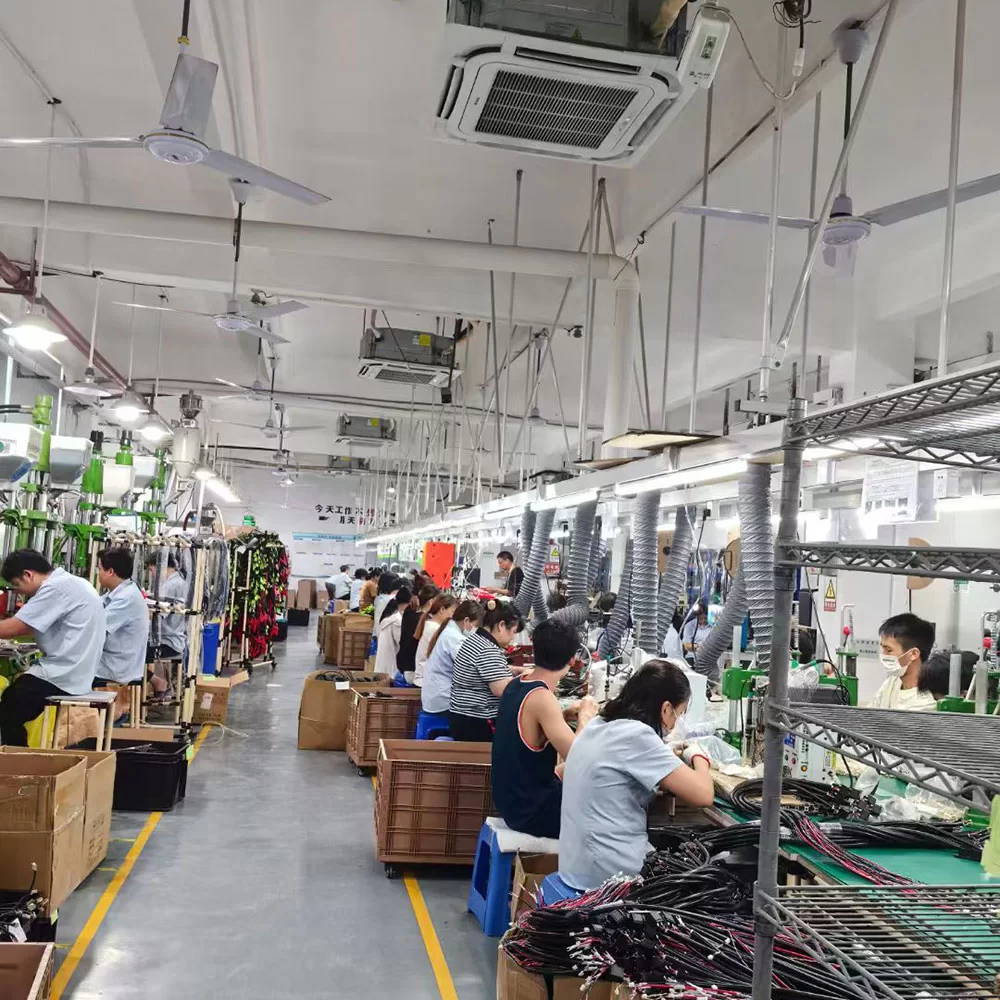
The cable & wire harness assembly manufacturing process includes wire cutting, insulation stripping, wire stripping, splice, twisting, tinning, soldering, inner mold shaping, wire twisting, terminal crimping, sleeving, loop testing, tubing, cable tying, injecti onmolding, labeling, conduit threading, coiling, packaging, and AQL Inspection. However, not every process incorporates all these steps. The specific workflow is determined by the client’s design requirements, ensuring a customized approach to each cable assembly project.
Applications for Custom Wire Harness Assembly
Military and Aerospace
Vehicles require specialty cables and wiring that can withstand extreme temperatures, altitudes, and environments. These extra-rugged assemblies are found in aircraft, missiles, spacecraft, military vehicles, and more.
Agriculture
Most heavy farm equipment uses wiring harnesses, including tractors, cultivators, sorters, and balers. We use UV- and chemical-resistant cables with durable fastenings to protect agricultural harnesses from the impact of heavy use and exposure to outdoor elements, ensuring that harnesses work at full capacity all season.
Robotics
Custom wire harness assembly for robotics often presents complex design for manufacturability and manufacturing challenges. The assemblies are often small and intricate but must still be durable and flexible enough to accommodate the robot’s full, repeated range of motion.
Oil and Gas
It would be difficult to create an exhaustive list of harness applications in the oil and gas industry: derricks, wells, platforms, and telemetry systems all rely on such assemblies in multiple ways. For these intense applications, we prioritize durability, corrosion resistance, easy installation, and maintenance in our designs for manufacturability.
Telecommunications
The telecommunications industry commissions some of the most rugged wire harnesses available. These applications require custom wire harness assembly that can withstand high loads of data and electricity while standing up to environmental wear.
Transportation
The transportation industry relies on wire harness assemblies to power a wide range of vehicles, from cars and trucks to airplanes and trains. Our wire harnesses are designed for manufacturability to withstand high vibrations, extreme temperatures, and harsh weather conditions, making them the ideal choice for reliable and long-lasting performance in these demanding environments. Our customized designs for manufacturability allow for efficient routing of wires within the vehicle or aircraft, maximizing space and reducing potential damage.
Automotive
Automotive applications present unique challenges, often encompassing miles of wiring that must be installed properly to prevent electrical failures. For this reason, all vehicles, whether consumer, commercial, or industrial, require expert custom wire harness assembly manufacturing.
Medical
The medical industry presents multiple custom wire harness assembly challenges, especially since malfunctions can cause patient injury or even death. Harnesses for electro-medical equipment, irradiation apparatus, and in-vitro diagnostic equipment must be designed for manufacturability for high signal integrity with an emphasis on reliability. Many of the medical harnesses we manufacture use Teflon or silicone for durability and feature specialty safety jacks, bio-sensitive components, and disposable elements.
OEM Manufacturing
Wiring harnesses facilitate many manufacturing processes, including robotic assembly methods and yield enhancement equipment. Specialized harnesses in this industry can protect product quality while also increasing operational efficiency.
What’s the Difference Between a Wire Harness and a Cable Assembly?
Wire harness is an organized bundle of discrete wires, connectors, and terminals designed to route electrical signals efficiently within a system. It typically uses low-voltage wiring secured by cable ties, lacing, or heat-shrink tubing to maintain structure.
Cable assembly encases its wires in a unified outer sheath or jacket for added protection against heat, abrasion, and environmental stress. These assemblies often integrate shielding, strain relief, and molded connectors to support harsher conditions or higher-performance requirements.
The requirements and restrictions of the intended application determine whether a wire harness or cable is more appropriate:
Cable assemblies are ideal for use in applications that involve harsh operating or environmental conditions, such as excessive heat, moisture, friction, compression, abrasion, etc.
Wire harnesses are ideal for applications that require a low-cost organizational solution and involve minimal exposure to harsh conditions.
Wire Harness Assembly Process
1. Design
Design is the first step. Engineers create electrical schematics and wiring diagrams based on how the equipment will be used. The design includes current levels, wire lengths, wire gauge, insulation materials, connector positions, and routing paths. All this information is laid out on a wire harness assembly board, which is used as a reference during production. The design also considers factors like heat dissipation, safety, ease of manufacturing, and available space.
- 2. PrototypingBefore mass production, a prototype is made. Engineers test its electrical performance and structural layout to check if the design works well. If any issues are found, the design can be improved. Prototyping helps avoid errors in later stages and increases the overall reliability of the cable and harness assembly.
- 3. Wire Cutting and PreparationUsing automated cutting machines, wires are cut to the required lengths according to the diagram. Each wire is labeled or marked for easy identification. Then, the insulation at both ends of the wire is stripped to expose the metal core, making it ready for terminal crimping. Accurate length and clean preparation are important for the quality and performance of the wire harness assembly.
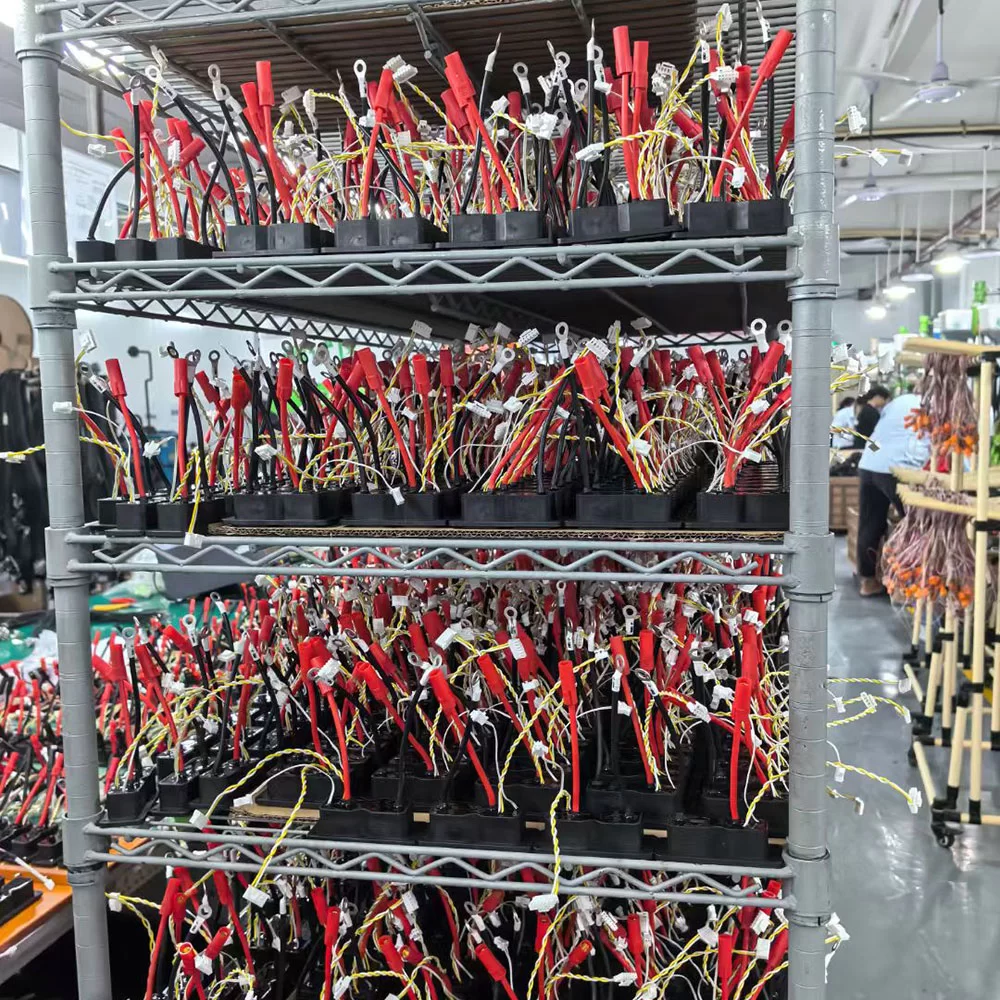
- 4. Terminal Crimping and Connector InsertionStripped wires are crimped with terminals using either manual tools or automated equipment. After crimping, wires are inserted into the right connector or module according to the wiring diagram. Good terminal crimping is essential for stable electrical connections, especially in high-vibration environments like cars.
- 5. Harness Layout and AssemblyOnce wires are ready, workers place them on the wire harness assembly board as per the design. The wires are routed, branched, and fixed in place. After wiring, protective materials like heat shrink tubing, tape, and sleeves are applied to form a neat and compact wire assembly. This step improves installation efficiency and makes future maintenance easier.
- 6. Electrical TestingAfter the harness is assembled, electrical testing is done. This includes continuity tests, insulation resistance checks, and short-circuit detection. These tests make sure there are no loose connections, miswires, or open circuits. In industries with strict requirements like automotive or medical, additional high-voltage or interference tests are also performed to ensure the harness works reliably in harsh conditions.
- 7. Quality ControlOnce the harness passes electrical tests, a final quality inspection is carried out. This includes checking appearance, measuring dimensions, and confirming structural integrity. In critical fields like aerospace and automotive electronics, extra tests like thermal cycling, vibration simulation, and aging tests may be added to ensure every electrical harness meets industry standards and works reliably over time.
Challenges in the wire harness assembly process:
Complexity of designs:
Electrical systems are becoming more advanced every day, and thus, their designs are also becoming intricate. To support the electrical functions of such complex systems, wire harness manufacturers must manufacture harnesses that can help a wide range of electrical tasks within a limited space. Precise wiring paths, careful routing, and multiple terminations complicate the assembly process.
Environmental factors:
Temperature fluctuations in vehicles, automotive, and aerospace systems can degrade wires over time. A sudden change of temperature from cold to extremely hot can affect the flexibility and insulation of the wire. This can lead to short circuits, crackling, or reduced electrical performance. Manufacturers need to be wary of such variations to ensure the reliability and longevity of electrical systems.
Choosing the right materials:
A wire harness assembly comprises different materials for different components, and every material should be chosen keeping in mind the specific functionality of that material in its component. Factors like temperature tolerance, flexibility, resistance to moisture/chemicals, ability to handle mechanical stress, etc., should be considered to ensure the product’s longevity.
If you have any camping barbeque equipment inquiry, please feel free to contact us.
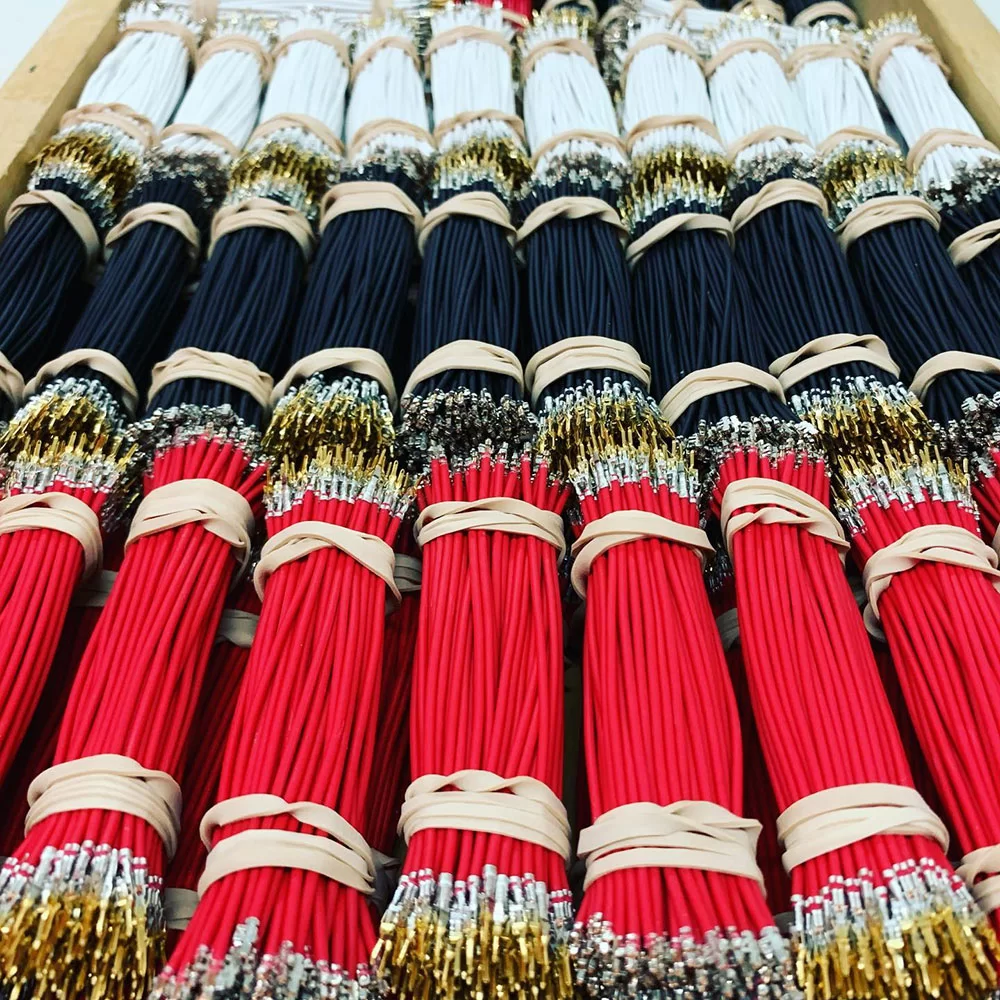

Managing kitting and packaging in-house can be time-consuming, costly, and error-prone.

Maybe an off-the-shelf cable can't meet your needs.
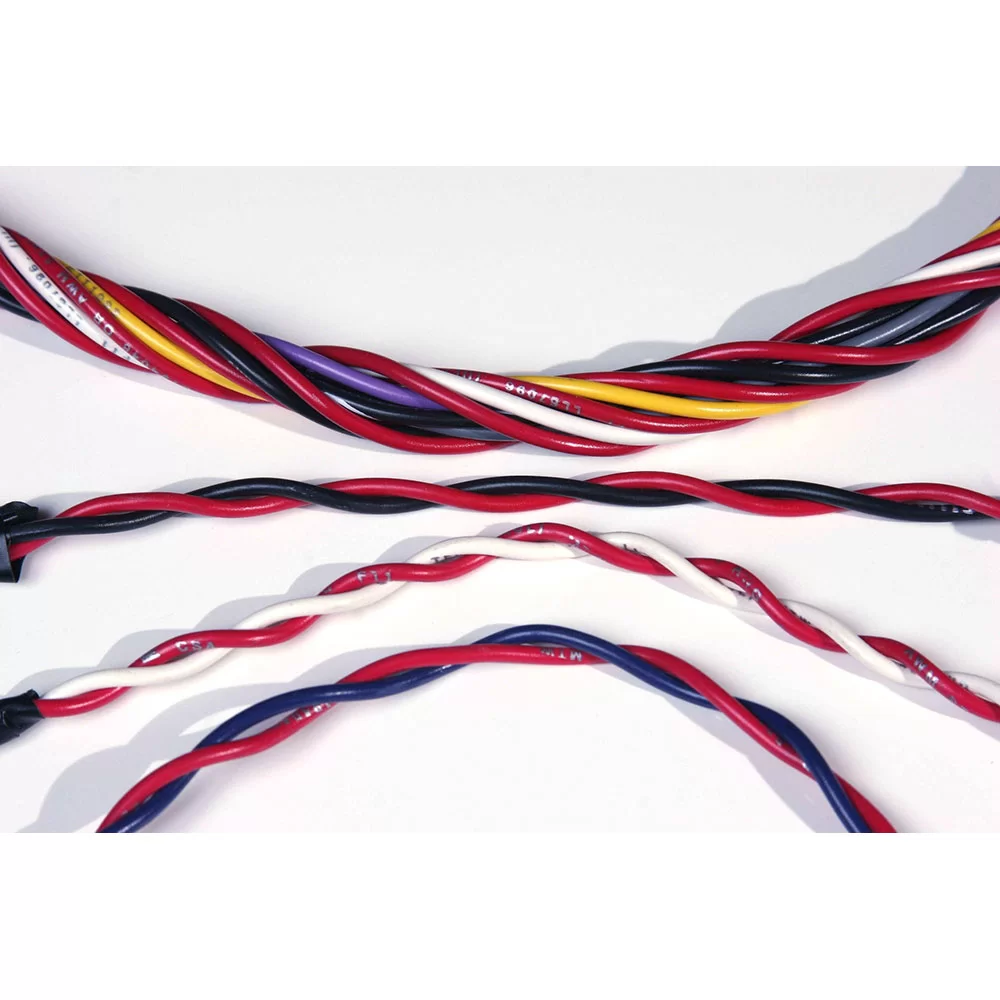

Twisting entwines multiple wires and arranges them tightly next to each other. Depending on the AWG size, we can group up to fifty conductors.

Shielding refers to the metallic layer surrounding a cable’s conductor, created to limit signal interference between the wire and external fields.
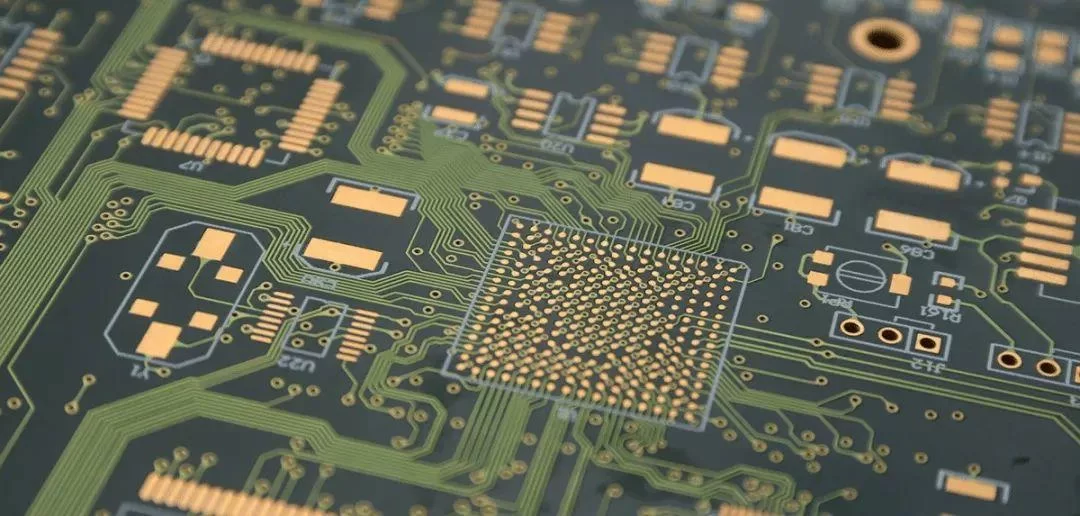
PCB manufacturing is the process of building a physical PCB from a PCB design according to a certain set of specifications.
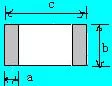
The following design standards refer to the IPC-SM-782A standard and the design of some famous Japanese design manufacturers and some better design solutions accumulated in the manufacturing experience.
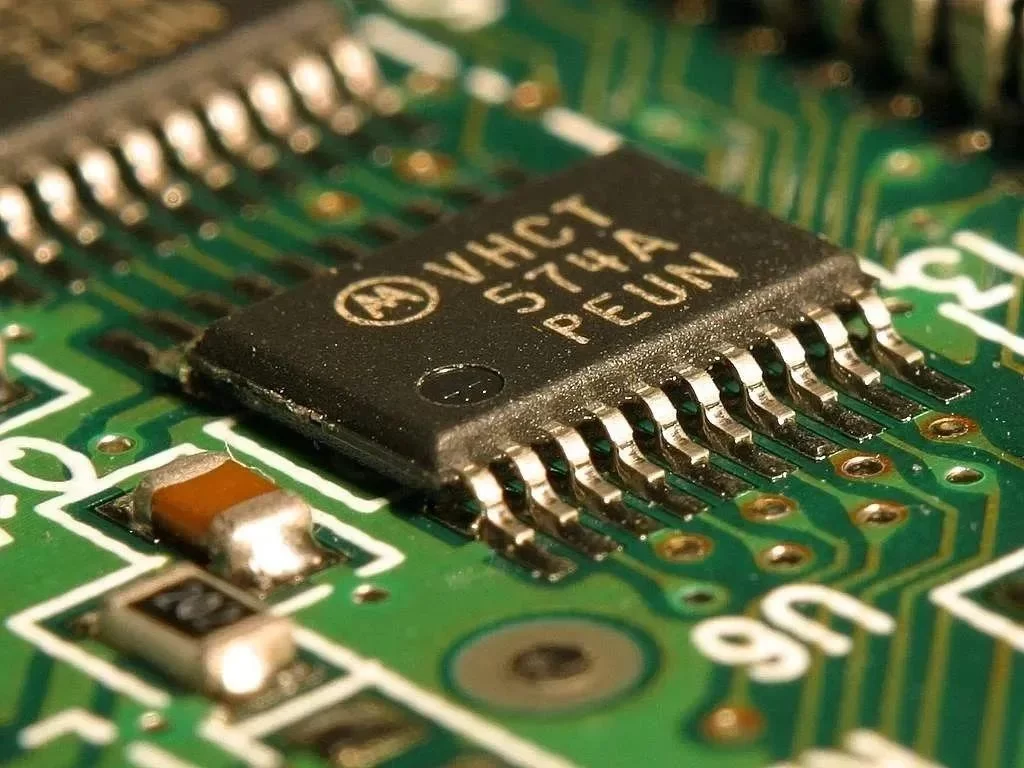

Via holes, also known as through holes, play a role in connecting different parts of a circuit board.