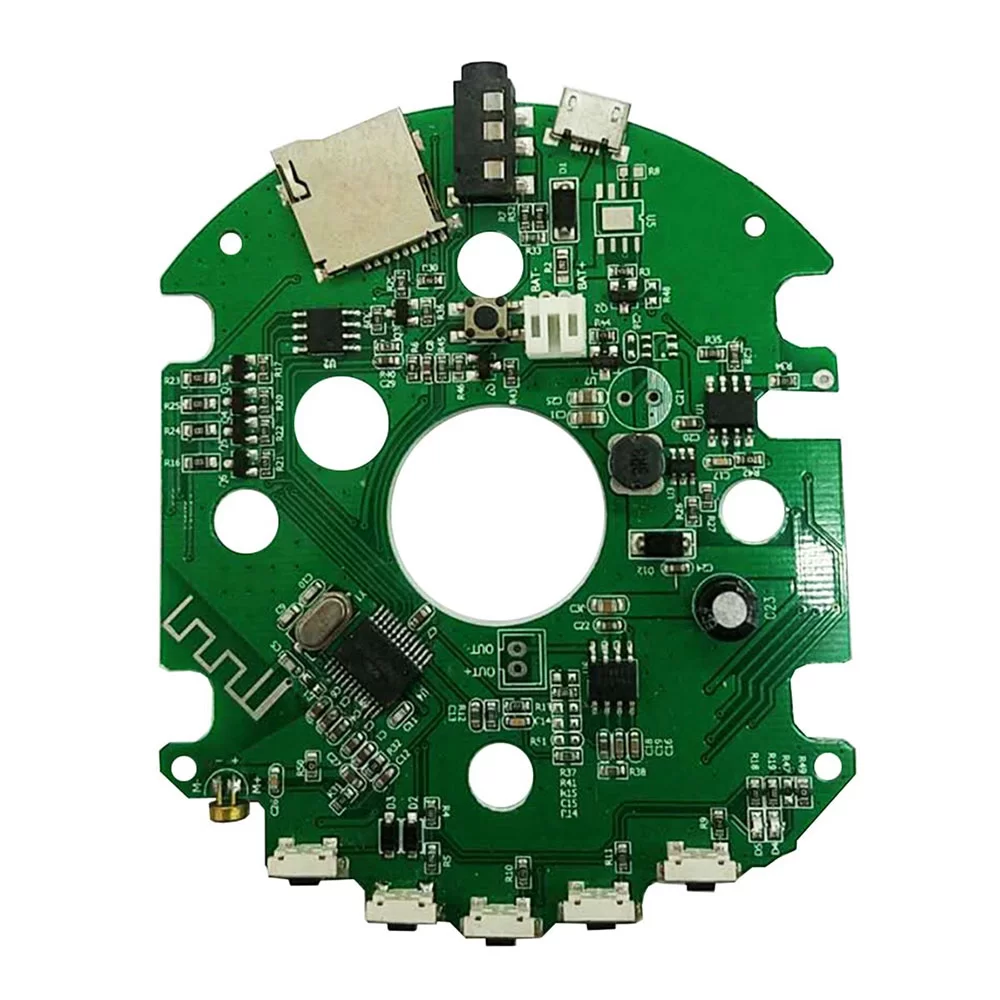
Programming Education Board Assembly
What are the differences between Programming education boards Assembly and other PCB Assembly?
The main differences between PCB assembly for programming education boards and other general PCB assemblies lie in design goals, component types, assembly processes, and application scenarios.
1. Design Goals and Complexity: PCB assembly for programming education boards typically simplifies design to reduce costs and improve ease of use, making it suitable for beginners in programming and electronic experiments. For example, the DeskHop open-source project emphasizes low cost and modular teaching, supporting a complete learning process from source code compilation to firmware flashing.
General PCB assembly may target high-density, high-performance requirements, such as industrial PLC control systems that need to meet stringent requirements for anti-interference and wide-temperature operation, resulting in more complex designs.
- 2. Component Types and Assembly Processes: Programming education boards commonly use standard package components such as 0805 and 0603 to reduce procurement and assembly difficulty, making them suitable for manual or semi-automatic soldering. For example, Arduino-compatible boards can be quickly assembled on breadboards, facilitating prototyping.General PCB assembly may involve high-density packages such as BGA and QFN, requiring fully automated SMT equipment and reflow soldering processes to achieve higher assembly density and reliability.
- 3. Testing and Functional Verification: Post-assembly testing of the programming education board focuses on verifying basic functions, such as power supply testing, communication testing, and USB interface checks, facilitating quick learning for students.Ordinary PCB assembly requires rigorous electrical testing (such as AOI and X-ray inspection) and aging tests to ensure long-term reliability and compliance with industry standards such as IPC-A-600.
- 4. Application Scenarios and Flexibility: Programming education board assembly emphasizes open source and scalability, supporting teaching tasks such as firmware modification, PCB design optimization, or adding peripherals (such as OLED screens).Ordinary PCB assembly focuses more on mass production efficiency, mechanical strength, and environmental adaptability, such as for aerospace or industrial equipment requiring highly durable connections.
Programming education Board PCB Assembly
The Role of PCBs in Programming education Board
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) form the foundational technology in Programming education Board, enabling interactive learning tools, digital devices, and laboratory instruments to function efficiently and reliably. By providing a compact, organized platform for electrical connections and component integration, PCBs support the delivery of consistent performance and user-friendly interfaces essential for educational settings.
1. Enabling Interactive and Digital Learning
PCBs integrate microcontrollers, sensors, and display modules that power interactive devices such as tablets, electronic whiteboards, and learning kits.
They facilitate real-time feedback, multimedia content delivery, and adaptive learning experiences.
2. Supporting Laboratory and Experimental Instruments
In educational labs, PCBs provide the backbone for measurement, control, and data acquisition systems, ensuring accuracy and repeatability in experiments.
Robust PCB designs allow for reliable operation despite frequent handling and diverse environmental conditions.
3. Facilitating Connectivity and Communication
PCBs enable wired and wireless connectivity modules, allowing Programming education Board to connect to networks, share data, and integrate with learning management systems.
4. Enhancing Durability and Safety
Programming education Board PCBs are designed to meet strict safety standards and incorporate protective features to ensure safe use by students.
Durable materials and coatings help devices withstand frequent use and handling.
5. Allowing Cost-Effective Mass Production
The standardized manufacturing of PCBs helps keep educational equipment affordable while maintaining quality and performance across large volumes.
Future Implications of Programming education PCB Assembly
As educational technology continues to advance, PCB assembly for educational equipment is expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in transforming learning environments. Several trends and innovations are set to shape the future:
1,Integration of Smart and Interactive Technologies
The growing adoption of AR/VR systems, AI-driven tutoring tools, and IoT-enabled classroom devices will demand highly specialized PCB designs with increased processing power, wireless capabilities, and sensor integration.
2,Miniaturization and Portability
Portable and modular learning devices will require compact, lightweight PCBs with flexible designs, enabling students to learn anytime and anywhere without sacrificing functionality.
3,Enhanced Connectivity
The rise of cloud-based education and remote learning platforms will push for PCBs with robust wireless modules (Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 5.3, 5G), ensuring fast and stable communication between devices and learning platforms.
4,Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Designs
With environmental awareness becoming a priority, educational institutions will increasingly prefer PCBs made from lead-free materials, recyclable substrates, and energy-efficient components.
5,Customizable and Adaptive Hardware
Future educational PCBs will likely feature modular architectures, allowing institutions to adapt or upgrade hardware for different courses, levels, or technologies without replacing entire systems.
6,Improved Reliability and Longevity
As educational budgets tighten, demand for PCBs with extended lifespans, low maintenance requirements, and strong resistance to wear and tear will grow.
In short, the future of education industry PCB assembly will be characterized by smarter, greener, and more adaptable designs, directly influencing the way students learn and teachers teach.
If you have any camping barbeque equipment inquiry, please feel free to contact us.

Managing kitting and packaging in-house can be time-consuming, costly, and error-prone.

Maybe an off-the-shelf cable can't meet your needs.
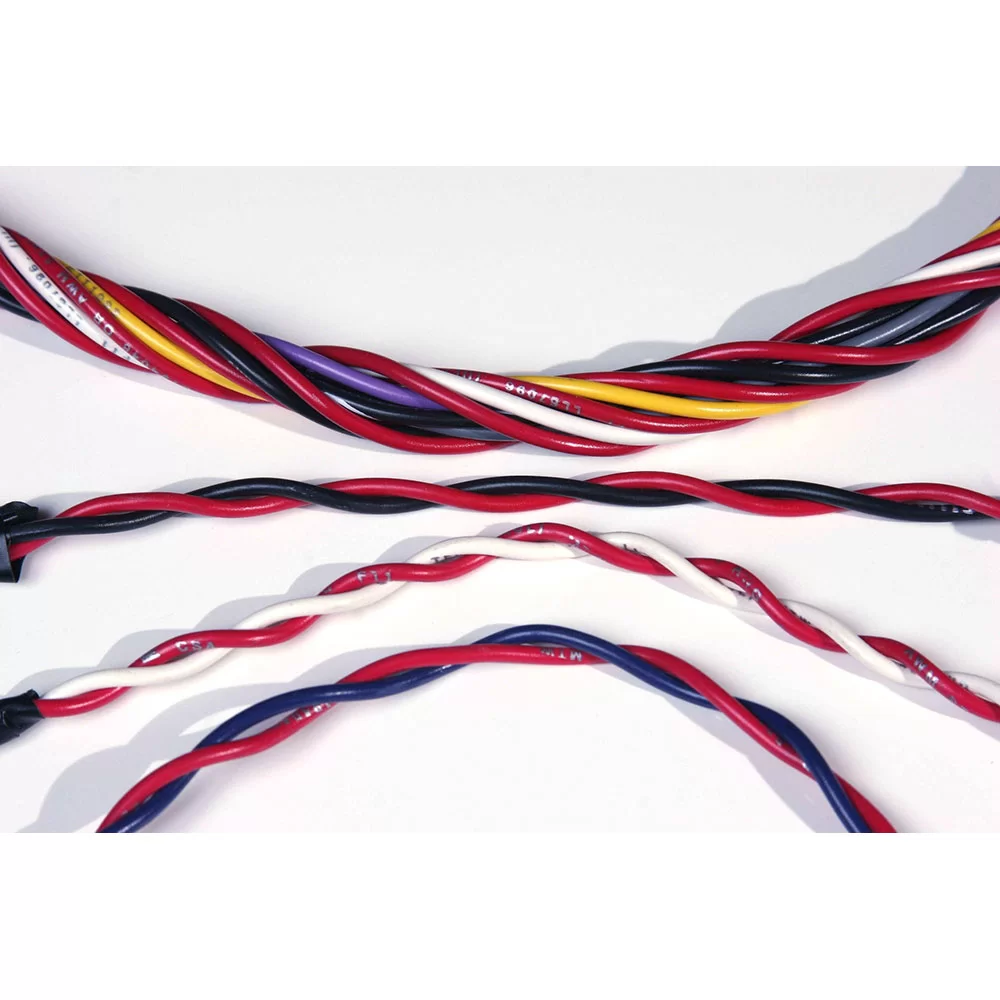

Twisting entwines multiple wires and arranges them tightly next to each other. Depending on the AWG size, we can group up to fifty conductors.

Shielding refers to the metallic layer surrounding a cable’s conductor, created to limit signal interference between the wire and external fields.
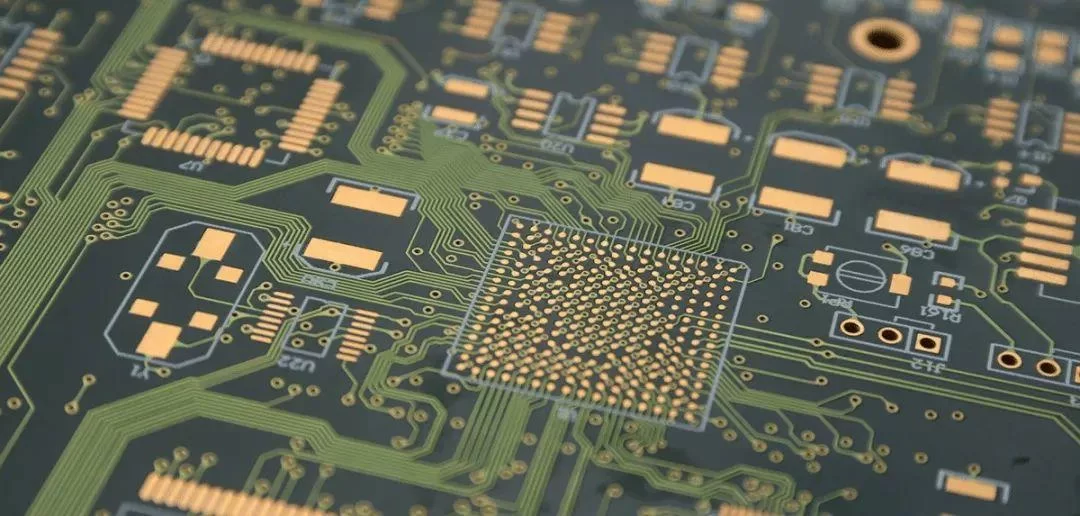
PCB manufacturing is the process of building a physical PCB from a PCB design according to a certain set of specifications.
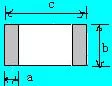
The following design standards refer to the IPC-SM-782A standard and the design of some famous Japanese design manufacturers and some better design solutions accumulated in the manufacturing experience.
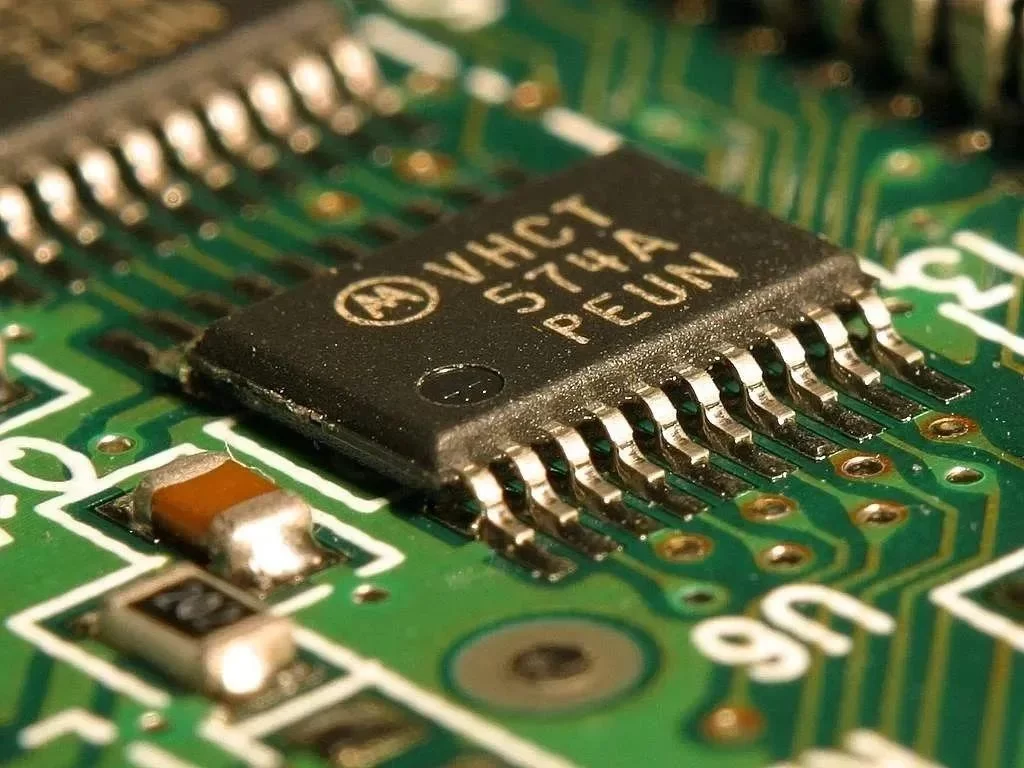

Via holes, also known as through holes, play a role in connecting different parts of a circuit board.