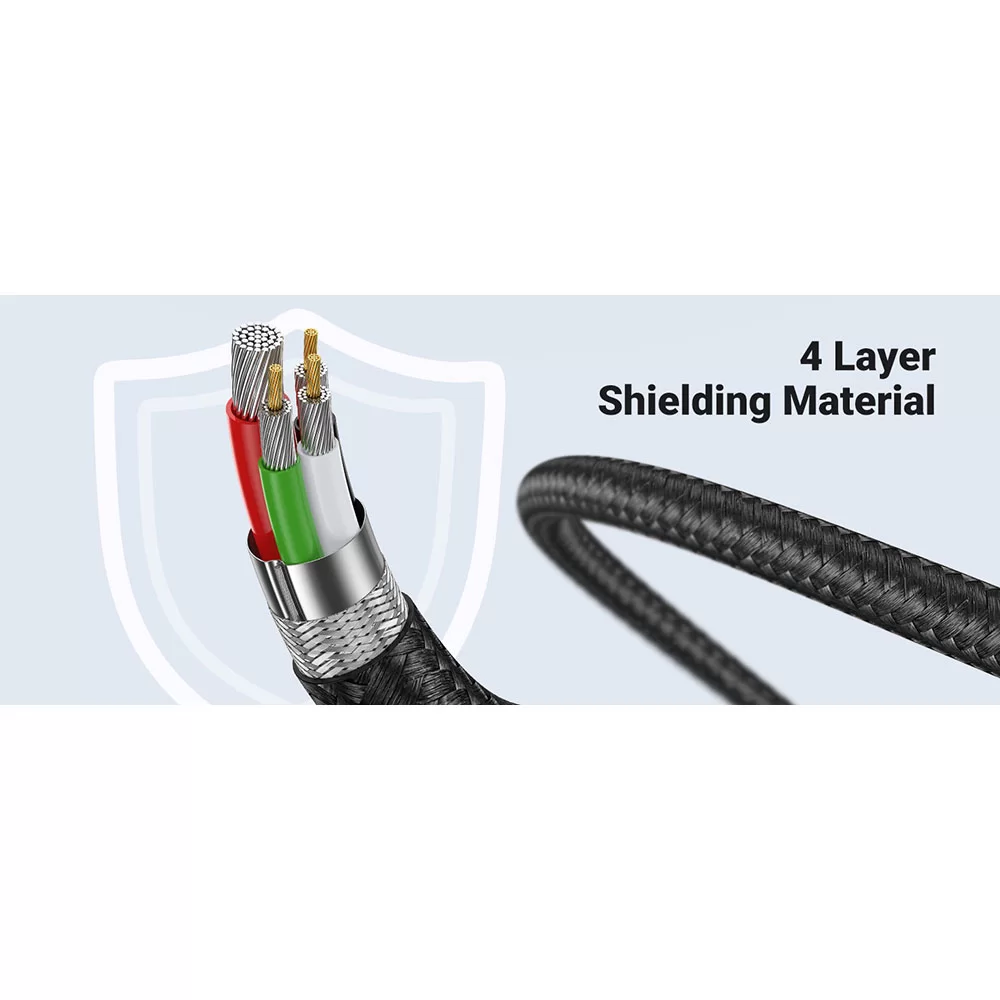
Shielding
Common Shield Materials
Shielding refers to the metallic layer surrounding a cable’s conductor, created to limit signal interference between the wire and external fields. Shielding plays an essential role in maximizing the effectiveness of cable systems and is designed to minimize signal leakage and the reception of signals produced by external sources.
Shields are available in a variety of conductive materials:
Bare copper
- Tinned copper
- Galvanized steel
- Stainless steel
- Aluminum foil
- Fiberglass
- Kevlar
Of these materials, aluminum and copper are the most common. Conductive nylon tapes, plastics, and textiles can also be used to minimize signal interference, but are less effective and less common than most other shielding materials.
Shields are also available in a number of styles that can be chosen to accommodate specific environments, desired wiring characteristics, and other shielding needs.
How to choose the Proper Shielding?
Low-Frequency Applications
Braid or spiral wire shields are often used for low-frequency applications (up to about 1MHz). For low-frequencies, the end-to-end electrical resistance of a shield is a crucial factor in its effectiveness. For example, microphone cables are often made with a spiral wire shield, because of its effectiveness at audio frequencies.
Medium-Frequency Applications
Braid shields are frequently used for medium-frequency applications (1 MHz to 100 MHz). Braid shield effectiveness depends on the coverage it provides– the tightness of the weave. Coverage from a braided shield ranges from 65 to 98 percent. Higher braid coverage results in better shield performance but costs more.
High-Frequency Applications
Combination shields are the best option for high-frequency applications (above 100HMz). By combining a braided shield with a foil shield, any energy leaks that would normally come from a braided shield alone are blocked.
The purpose of the shield is to ground any of the noise a cable has picked up. The cable shielding and its termination must provide a low-impedance path to the ground. A shielded cable that is not grounded allows disruptions that can raise impedance and lower the effectiveness of the cable.
If you have any camping barbeque equipment inquiry, please feel free to contact us.
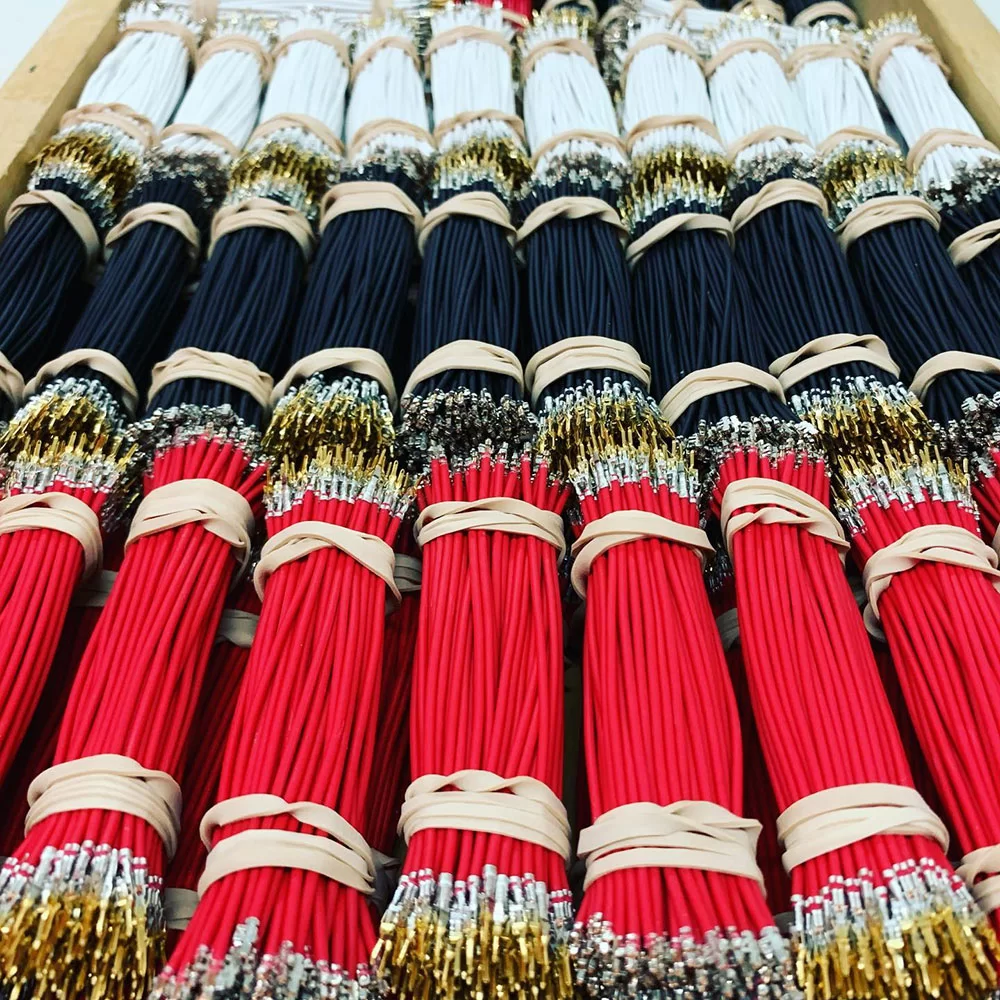

Managing kitting and packaging in-house can be time-consuming, costly, and error-prone.

Maybe an off-the-shelf cable can't meet your needs.
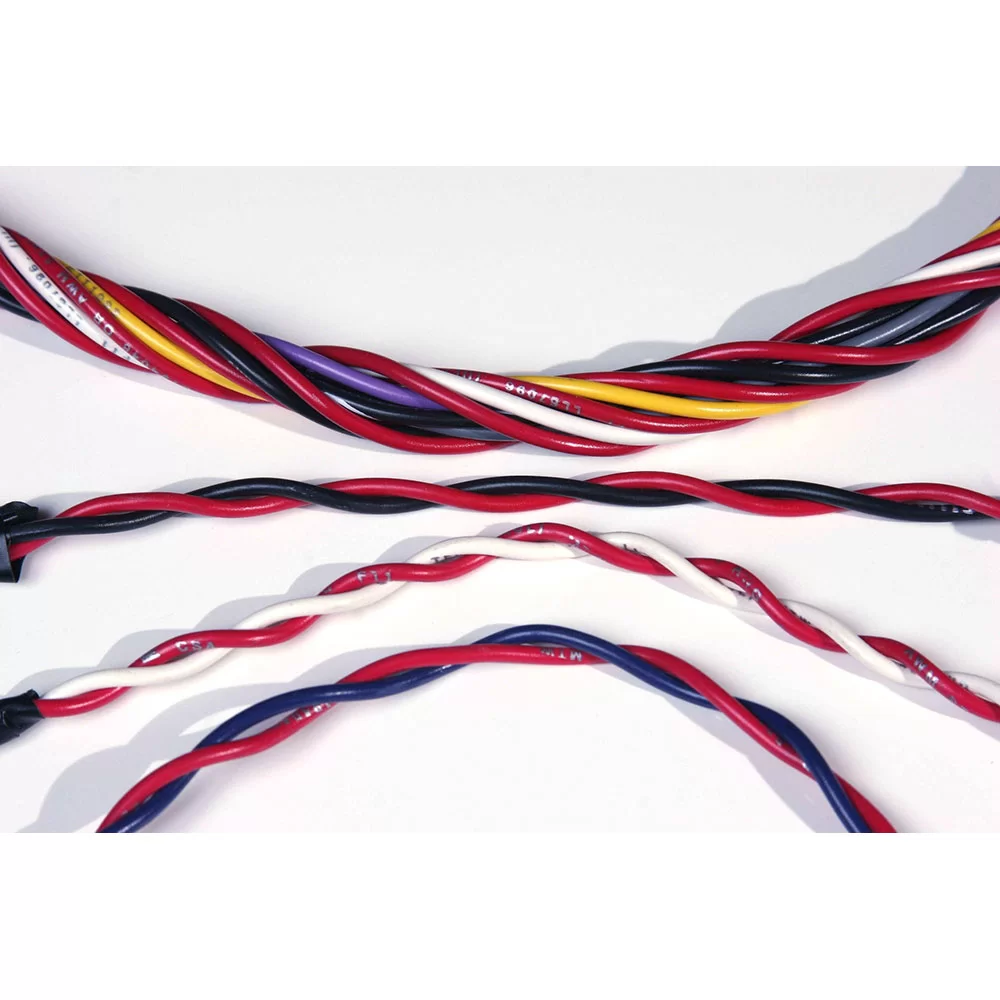

Twisting entwines multiple wires and arranges them tightly next to each other. Depending on the AWG size, we can group up to fifty conductors.
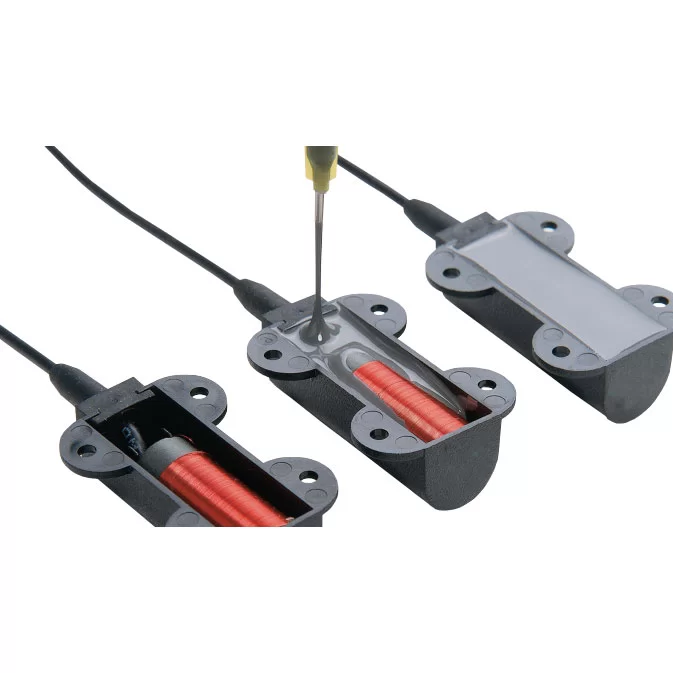

Cable potting involves encasing conductors in an epoxy, liquid, or gel within an enclosure or feedthrough housing.
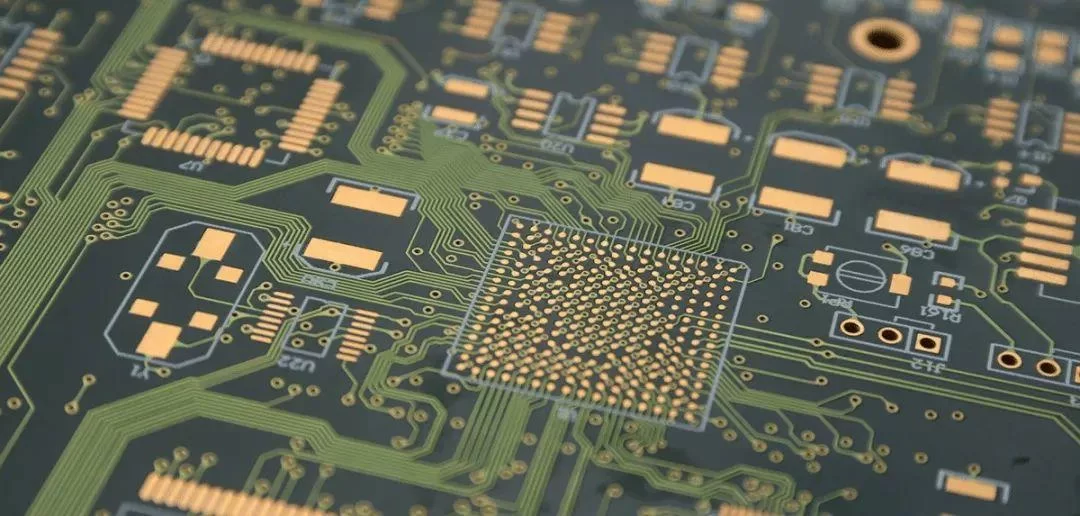
PCB manufacturing is the process of building a physical PCB from a PCB design according to a certain set of specifications.
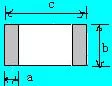
The following design standards refer to the IPC-SM-782A standard and the design of some famous Japanese design manufacturers and some better design solutions accumulated in the manufacturing experience.
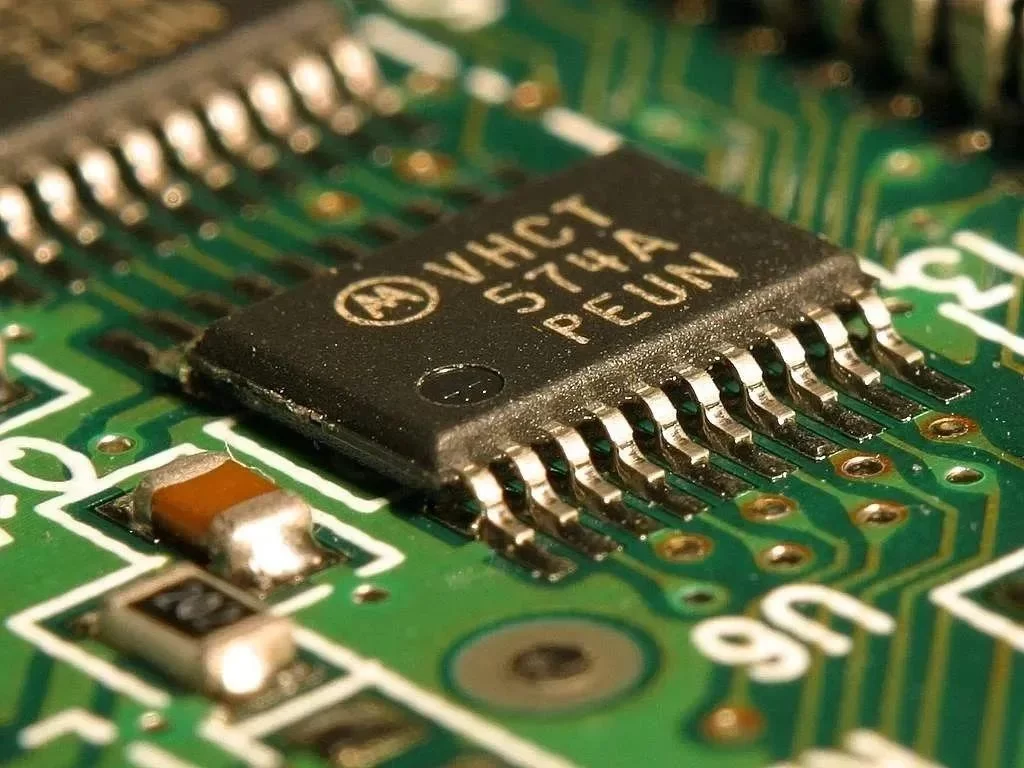

Via holes, also known as through holes, play a role in connecting different parts of a circuit board.