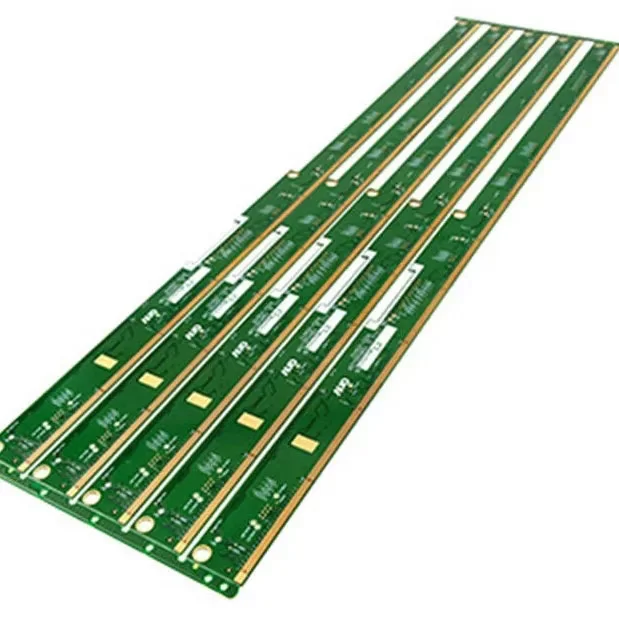
Long printed circuit boards (PCBs)
What's Long printed circuit boards (PCBs)
Long printed circuit boards (PCBs) represent a specialized segment of electronic manufacturing that addresses unique challenges in various industries. These extended form-factor PCBs, typically exceeding standard dimensions, have become increasingly important as electronic systems grow in complexity while simultaneously demanding greater integration. From telecommunications infrastructure to industrial control systems, long PCBs provide crucial connectivity solutions where conventional boards would be insufficient.
This comprehensive guide explores the world of long printed circuit boards—their design principles, manufacturing techniques, applications, and the future trends shaping their evolution. Whether you're an electronics engineer seeking to understand implementation challenges, a procurement specialist evaluating options, or a technical manager planning a new product development, this article offers valuable insights into the specialized domain of extended PCBs
Definition and Characteristics
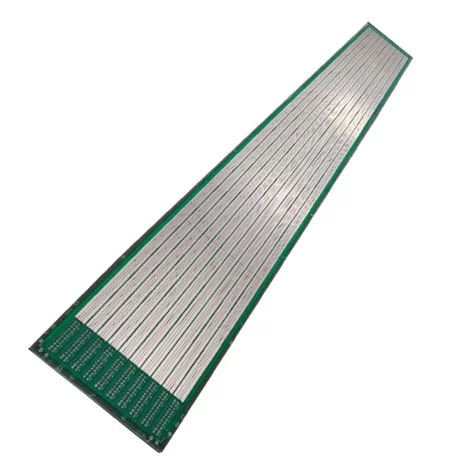
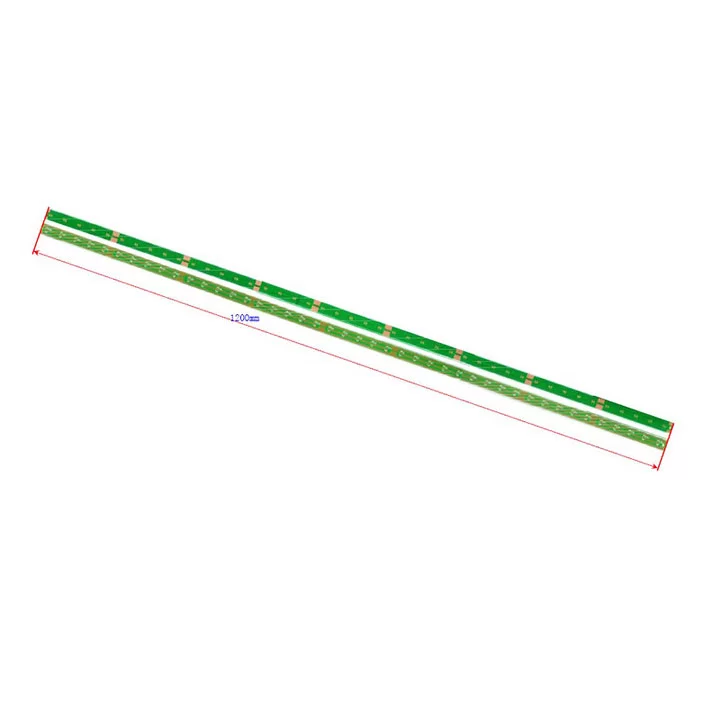
Long printed circuit boards refer to PCBs that significantly exceed standard dimensions in at least one direction. While the electronics industry has no universal definition of "long," these boards typically feature length-to-width ratios of 3:1 or greater, with lengths commonly exceeding 24 inches (610mm). Some applications may require lengths of several feet or even meters.
The key characteristics that distinguish long PCBs include:
Extended dimensions: Primarily increased length compared to typical PCB form factors
Specialized material requirements: Need for materials with superior mechanical properties to prevent flexing and warping
Design considerations: Addressing signal integrity concerns over extended distances
Manufacturing challenges: Requiring specialized equipment and processes for fabrication and assembly
Thermal management complexities: Managing heat dissipation across large surface areas
Types of Long PCBs
Long PCBs can be categorized based on their construction, material, and application requirements:
Standard Long PCBs: Single or double-sided boards with extended dimensions but conventional construction
Multilayer Long PCBs: Boards with multiple conductive layers, providing greater routing density in a long form factor
Flexible Long PCBs: Flexible or rigid-flex constructions that can bend while maintaining circuit integrity
Backplane Long PCBs: Specialized long boards used for interconnecting multiple circuit boards in a system
High-Frequency Long PCBs: Boards designed for RF or high-speed digital applications with extended dimensions
Applications and Use Cases
Telecommunications Infrastructure
Long PCBs are extensively used in telecommunications equipment:
Base Station Components: Extended backplanes for integrating multiple processing cards
Server Rack Systems: Long interconnect boards for data center infrastructure
Network Switches: Backplanes connecting multiple line cards
Signal Processing Systems: Extended boards for specialized telecom processing equipment
Industrial Control Systems
In industrial automation, long PCBs provide critical control infrastructure:
Motor Control Centers: Centralized control boards spanning multiple motor controllers
Process Control Systems: Extended interface boards connecting numerous I/O points
Power Distribution Units: Long boards for managing power in industrial settings
Factory Automation Equipment: Spanning extended production line control requirements
Transportation Systems
The transportation sector relies on long PCBs for various applications:
Railway Signaling: Extended control boards in railway infrastructure
Automotive Testing Equipment: Long boards in automotive diagnostic systems
Aerospace Control Panels: Extended boards for cockpit and flight systems
Marine Navigation Systems: Specialized long boards for maritime applications
Energy and Power Management
Long PCBs play vital roles in energy infrastructure:
Power Distribution Systems: Extended boards for monitoring and controlling power flow
Renewable Energy Inverters: Long boards for solar and wind power conversion
Smart Grid Components: Interface boards for grid management systems
Battery Management Systems: Long boards monitoring extended battery arrays
High-Performance Computing
In computing applications, long PCBs enable specialized configurations:
Supercomputer Backplanes: Extended interconnect boards for high-performance computing
Data Center Infrastructure: Long boards for server interconnection
Edge Computing Systems: Specialized long boards for distributed computing nodes
Artificial Intelligence Hardware: Custom boards for AI accelerator interconnection


If you have any camping barbeque equipment inquiry, please feel free to contact us.

Managing kitting and packaging in-house can be time-consuming, costly, and error-prone.

Maybe an off-the-shelf cable can't meet your needs.

Twisting entwines multiple wires and arranges them tightly next to each other. Depending on the AWG size, we can group up to fifty conductors.

Shielding refers to the metallic layer surrounding a cable’s conductor, created to limit signal interference between the wire and external fields.
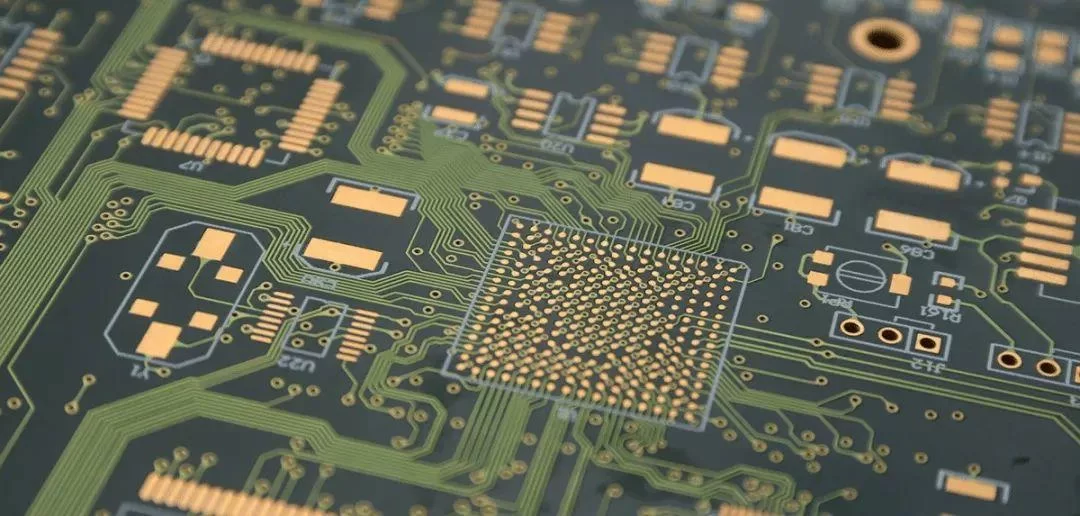
PCB manufacturing is the process of building a physical PCB from a PCB design according to a certain set of specifications.
The following design standards refer to the IPC-SM-782A standard and the design of some famous Japanese design manufacturers and some better design solutions accumulated in the manufacturing experience.
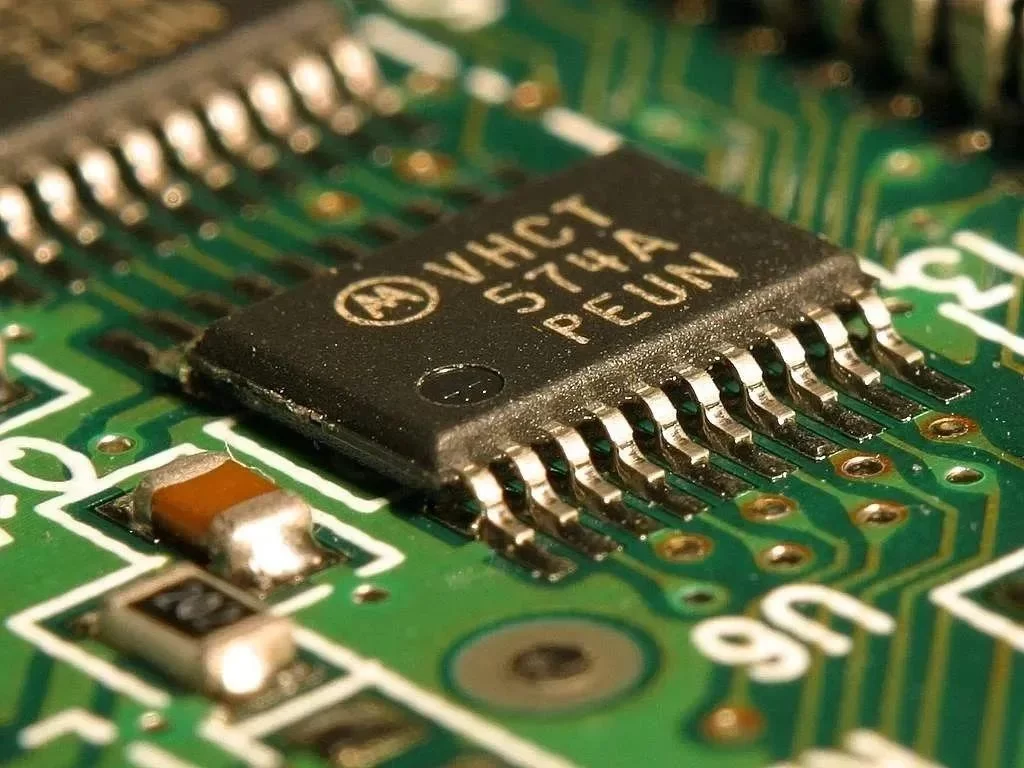

Via holes, also known as through holes, play a role in connecting different parts of a circuit board.