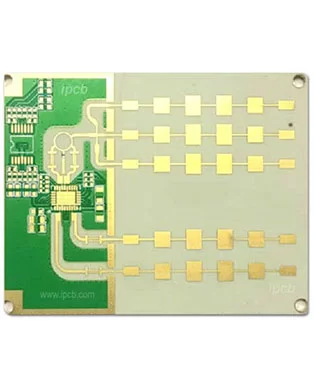
Radar PCB
Data Sheet
Model: Radar PCB
Material: Teflon/Ceramic PCB/Rogers/ITEQ IT180/Isola 370hr
- Quality standard: IPC-6012
- Dielectric constant: 2.0-16
- DK:3.48/3.0
- Layers:1 Layer -70 layer
- Thickness:0.254mm-6.0mm
- Copper thickness: 0.5OZ/1OZ
- Surface technology: Silver/Immersion Gold/OSP
- Application: Communication radar PCB,detection radar PCB
About Radar PCBs
Radar PCBs are critical components in all radar systems, as they handle data transmission, reception, processing, analysis, and result output. Consequently, radar circuit boards feature unique specifications—including multiple RF circuits—to enable fast, reliable data transfer.
Six Basic Components of Radar PCBs
Transmitter
The transmitter uses a power amplifier to amplify signals, so as to ensure the transmission power of radar lobes is strong enough. It is typically driven by an RF signal generator.
Receiver
The receiver uses a receiver processor (e.g., a superheterodyne receiver) to detect and process reflected signals, so as to ensure the radar can receive and analyze the signals reflected back from the target.
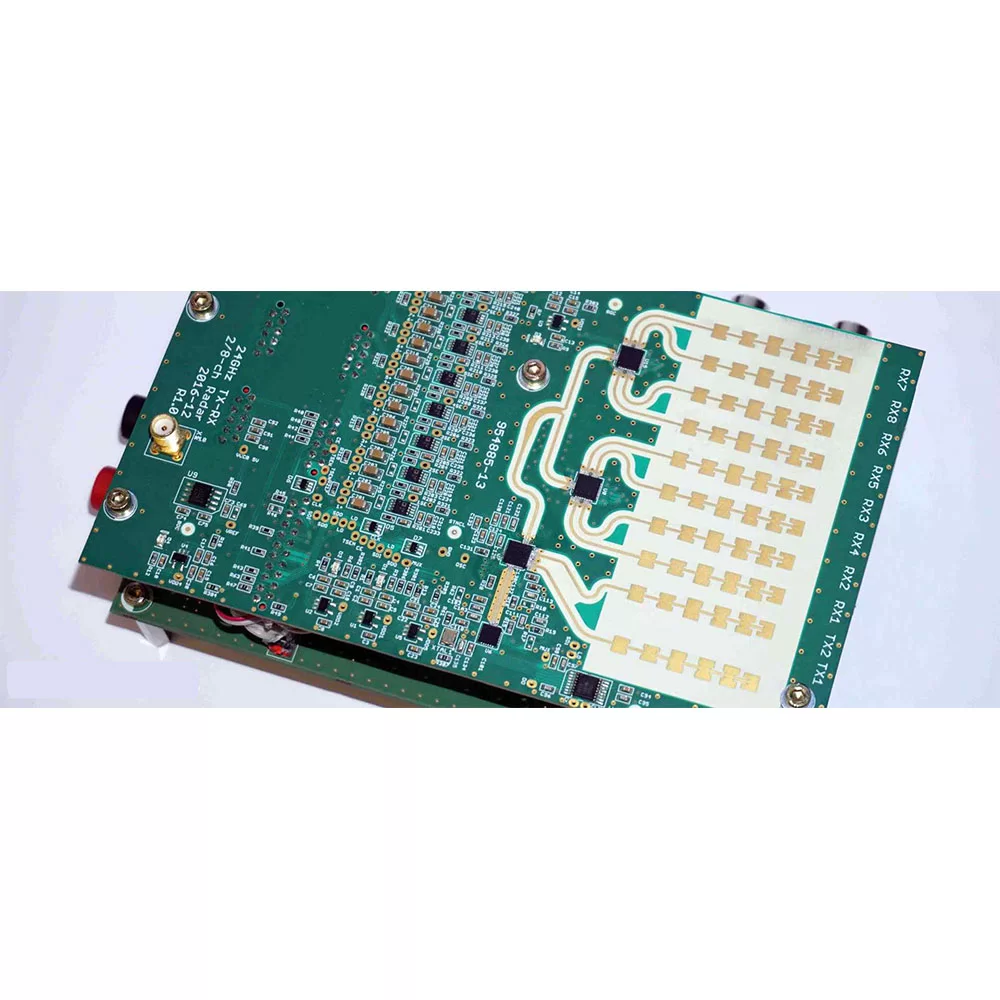
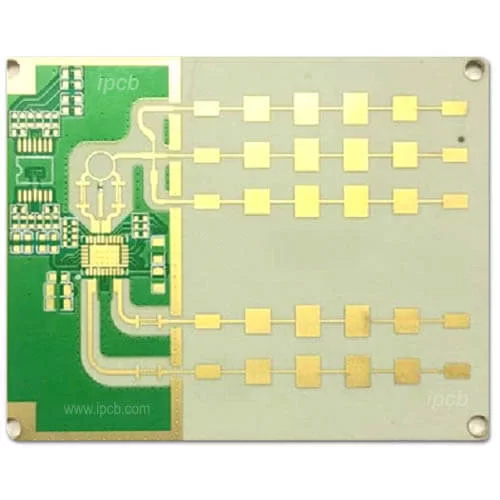
- AntennaThe antenna is responsible for transmitting and receiving radar waves. Depending on the radar’s design requirements, it can be a parabolic reflector, a planar array, or an electronically controlled phased array.
- DuplexerThe duplexer enables the antenna to switch between transmit and receive modes, so as to ensure the radar can transmit and receive signals effectively.
- WaveguideThe waveguide is a transmission line for transmitting radar signals, so as to ensure the signal remains stable and efficient during transmission.
- ThresholdDecision ModuleThe threshold decision module compares the receiver’s output with a threshold to determine the presence of a target. If the signal strength is below the threshold, it is deemed noise.
Types of common radar PCB
Monopulse Radar PCB: As one of the most common types, it directly measures the position of the target to ensure the accuracy of transmission and detection results.
- Doppler Radar PCB: It transmits electromagnetic waves to the target and determines the target's speed within a specific range based on the Doppler effect.
- Weather Radar PCB: It detects and analyzes weather conditions by transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals.
- Passive Radar PCB: Unlike active radars, it does not emit electromagnetic waves actively; instead, it detects, processes data from external illumination sources, and tracks targets.
- Pulse Radar PCB: It emits a series of high-intensity, high-frequency pulses, which enables high-precision target identification.
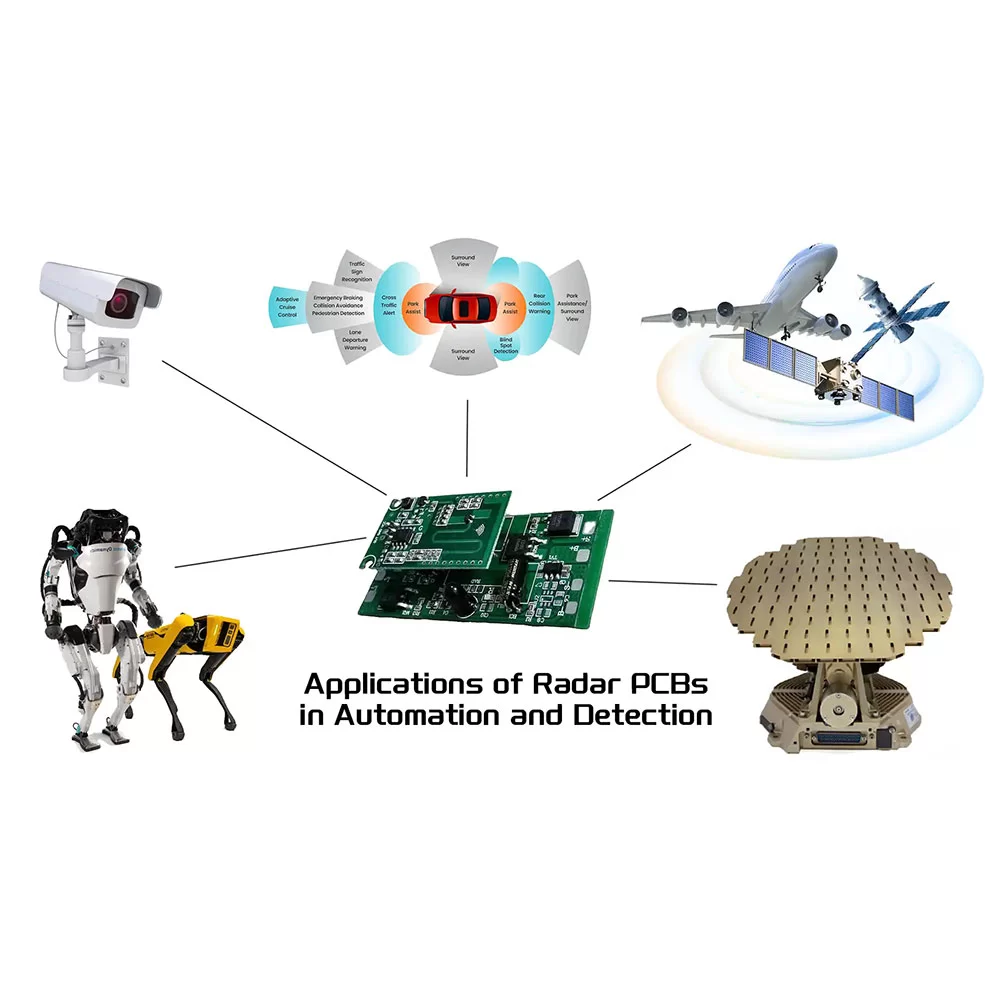
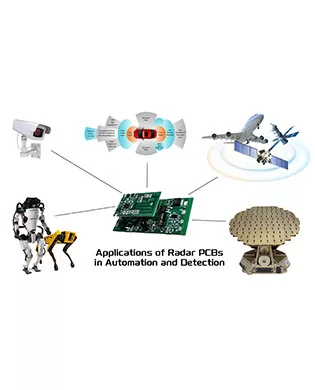
Application
1. Military Field
Radar PCBs are critical to safeguarding the security and precision of military operations—whether for missile guidance or identifying island, land, and maritime targets. They also deliver reliable signal processing for military surveillance and target tracking systems.
2. Civilian Applications
Radar PCBs are widely applied in civilian service systems: they enable traffic flow monitoring and regulation, as well as aircraft movement coordination in air navigation. They are also key components in autonomous driving and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS).
- 3. Space ApplicationsRadar PCBs support planetary monitoring and exploration, while ensuring the stable operation and navigation of spacecraft—laying a solid foundation for the success of space missions.
- 4. Security and ProtectionRadar PCBs are integrated into various security alarm systems for theft and fire prevention. They also bolster advanced sensing technologies, enabling smart home functions like automatic door opening and motion-activated lighting.
What are the challenges with radar PCB?
1. Radar PCBs have exceptionally high signal integrity requirements—even minimal deviations in routing or component placement can lead to substantial performance degradation.
- 2. Radar signals pass through multiple amplifiers, filters, and other analog circuits, demanding precise tuning and calibration.
- 3. Any noise or interference on radar PCBs can severely degrade radar performance, leading to false alarms and missed detections.
Guiding Principles for Radar PCB Design
Adhere to Applicable Regulations: Radar PCB designs must adhere strictly to local laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Select Components Appropriately: It is critical to choose components that align with the radar system’s performance requirements and overall design objectives.
- Minimize EMI: Incorporate targeted measures during design to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) from adjacent electronic devices and other interference sources.
- Choose Application-Specific Materials: Select materials that are optimally suited to the radar’s specific application scenarios and performance demands.
Benefits of using radar PCB
Improve signal integrity
Higher accuracy
- Reduce production cost
- Enhance sensitivity

If you have any camping barbeque equipment inquiry, please feel free to contact us.

Managing kitting and packaging in-house can be time-consuming, costly, and error-prone.

Maybe an off-the-shelf cable can't meet your needs.
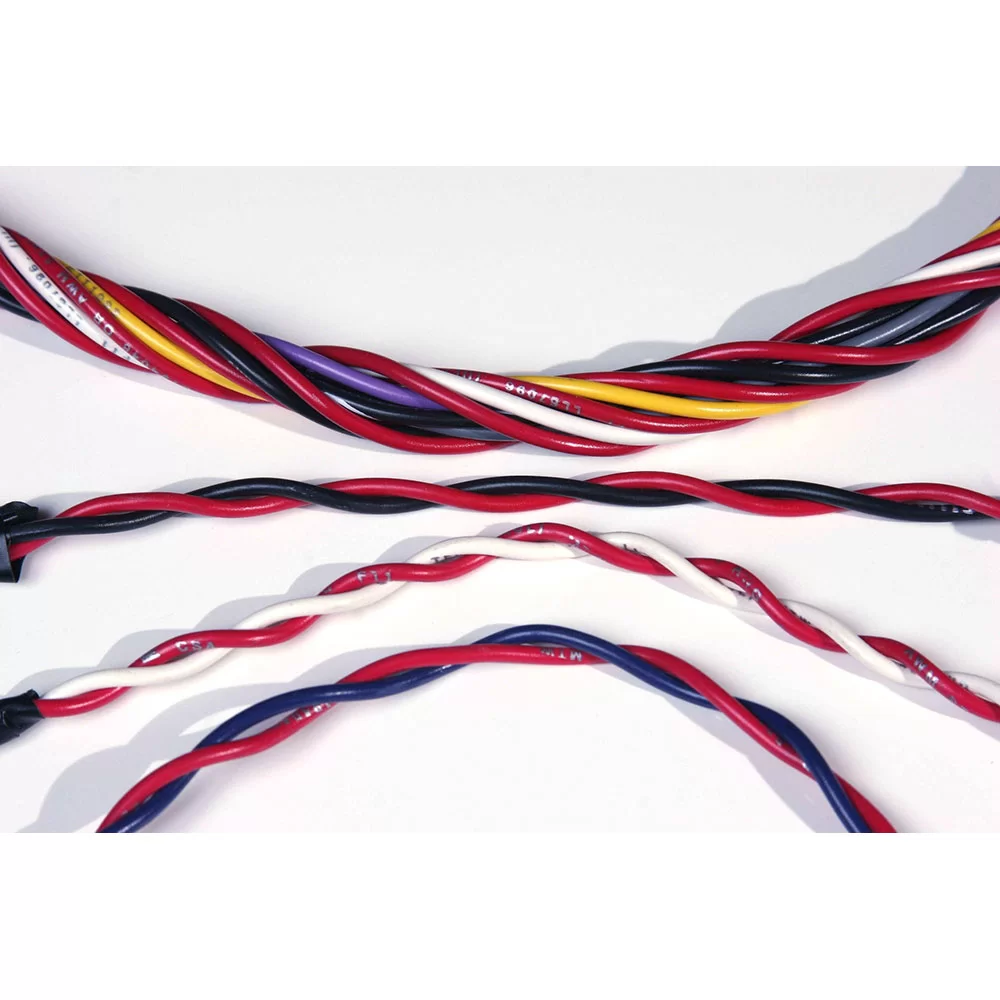

Twisting entwines multiple wires and arranges them tightly next to each other. Depending on the AWG size, we can group up to fifty conductors.

Shielding refers to the metallic layer surrounding a cable’s conductor, created to limit signal interference between the wire and external fields.
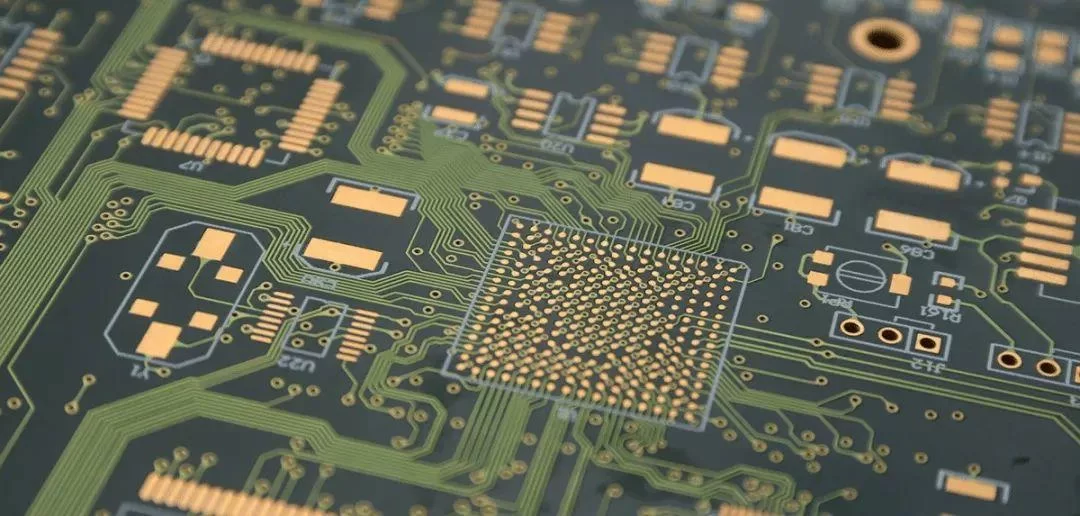
PCB manufacturing is the process of building a physical PCB from a PCB design according to a certain set of specifications.
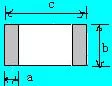
The following design standards refer to the IPC-SM-782A standard and the design of some famous Japanese design manufacturers and some better design solutions accumulated in the manufacturing experience.

Via holes, also known as through holes, play a role in connecting different parts of a circuit board.